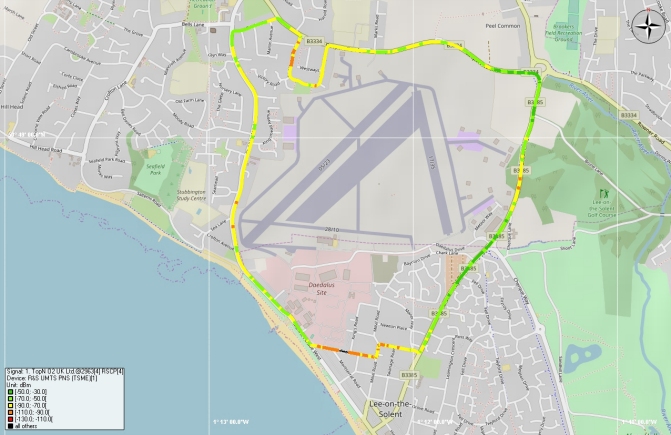
understanding of existing and likely coverage in and around proposed
developments, buildings and outdoor locations. Assessment of the likely impacts upon mobile phone
coverage and mobile network operations from wind turbines, wind
farms and other tall structures can also be undertaken. Such surveys can be used to support planning applications, discharge planning conditions or to enhance a building’s WiredScore Certification. Our survey equipment undertakes measurements of all key performance indicators of a 2G, 3G or 4G network, not just the signal strength of the received serving cell, which provides only a limited performance indication.
We also conduct automated high resolution in-building surveys with advanced mobile network signal receiving and processing hardware. Such surveys can be used to determine internal mobile network coverage, identify network coverage problems and to gain an understanding of signal penetration (or attenuation) through different building materials. Ofcom research undertaken in 2014 found; Broadly, building loss increases with frequency, i.e. higher frequency signals will experience a greater reduction in signal strength when passing through an object than lower frequency signals. This is the reason why lower frequencies are preferred for delivering wide area and in-building coverage for mobile networks; and The use of common materials such as foil-backed plasterboard and metallised double-glazing has a tangible effect on in-building coverage. On average, the presence of these materials reduced the strength of incoming signals by between 6 and 11 dB, compared to standard wall construction and single glazed windows.

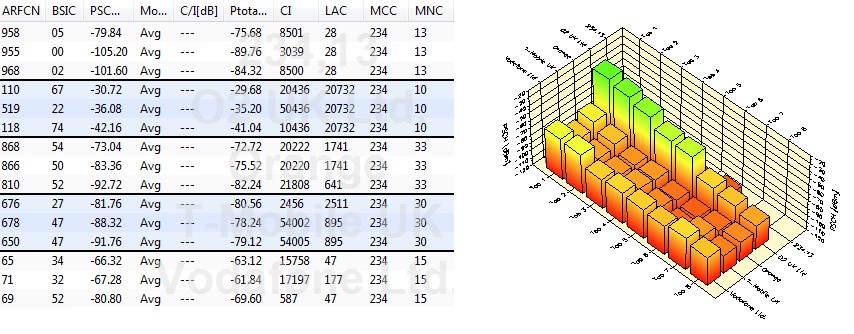
undertaken using advanced radio signal processing hardware with a Rohde & Schwarz TSMA and signal processing software from Rohde & Schwarz ROMES,
providing network owners with detailed analysis of network performance
and coverage. Reception testing can also be undertaken up to 13m AGL
using survey vehicles. Thames Water utilised this survey system between 2017 and 2023
to verify elevated 2G, 3G and 4G network coverage at a number of pumping
stations.
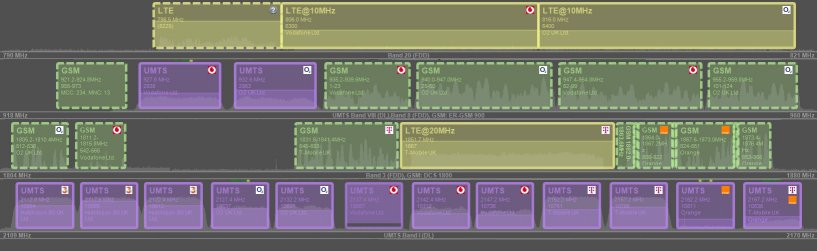
3G networks (3G, 3.5G and 3.75G – WCDMA / HSPA / HSPA+ / DC-HSPA+) find application in wireless voice telephony, mobile Internet access, fixed wireless Internet access, video calls and mobile TV. These are classed as (Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS)) networks and are based on wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA) technologies. They have been deployed worldwide as 3rd generation mobile communications systems. EE, O2, Three (Hutchison 3G UK Ltd) and Vodafone provide 3G services in the UK.
4G, short for fourth generation, is the fourth generation of mobile telecommunications technology, succeeding 3G and preceding 5G. Long Term Evolution (LTE) will ensure the competitiveness of UMTS for the next ten years and beyond by providing a high-data rate, low-latency and packet-optimized system. LTE can be operated in either frequency division duplex (FDD) or time division duplex (TDD) mode, also referred to as LTE FDD and TD-LTE. A 4G system, in addition to the usual voice and other services of 3G, provides mobile ultra-broadband Internet access, for example to laptops with USB wireless modems, to smartphones, and to other mobile devices. Conceivable applications include amended mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing and cloud computing. 4G networks are provided by EE, Three, O2 and Vodafone.